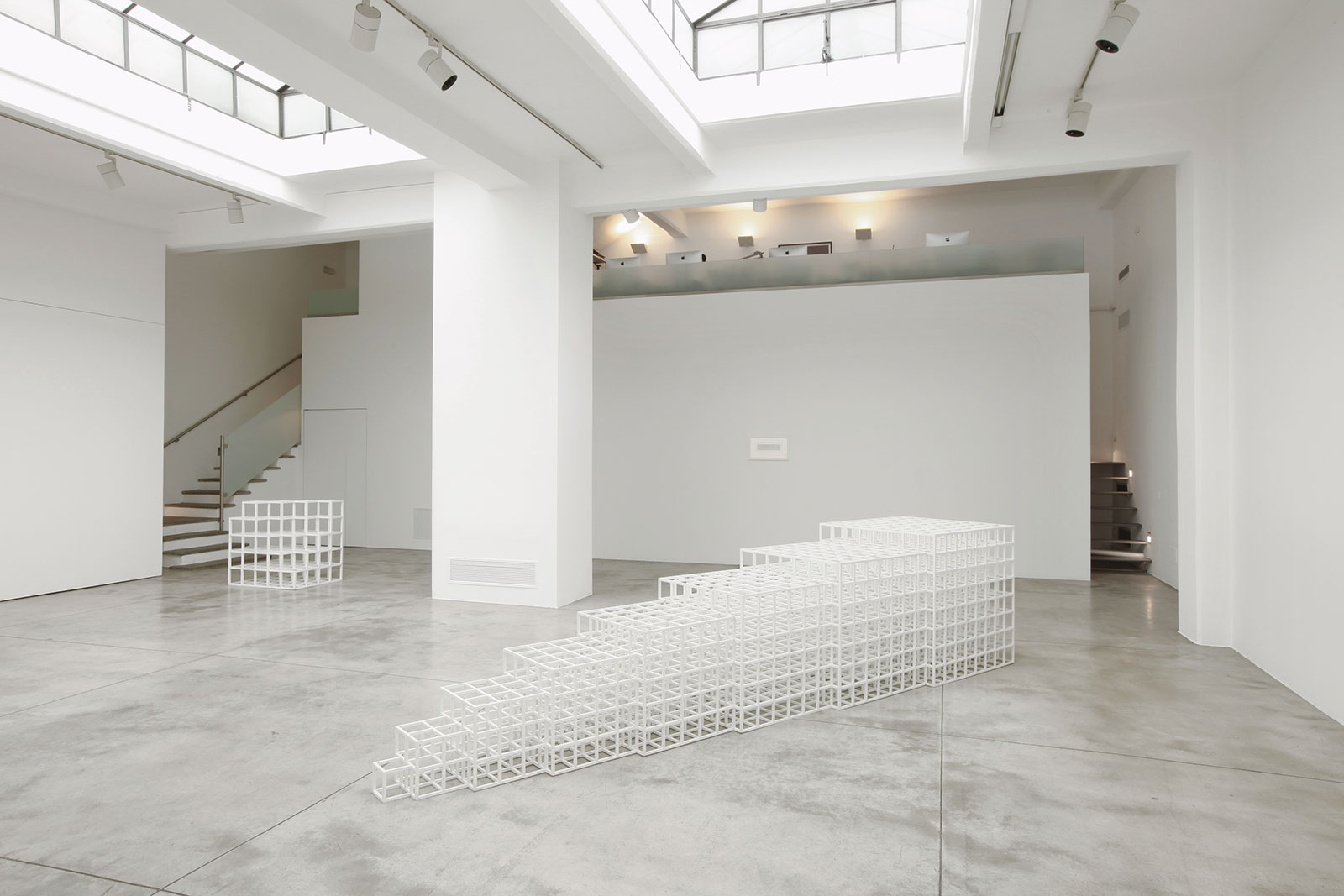
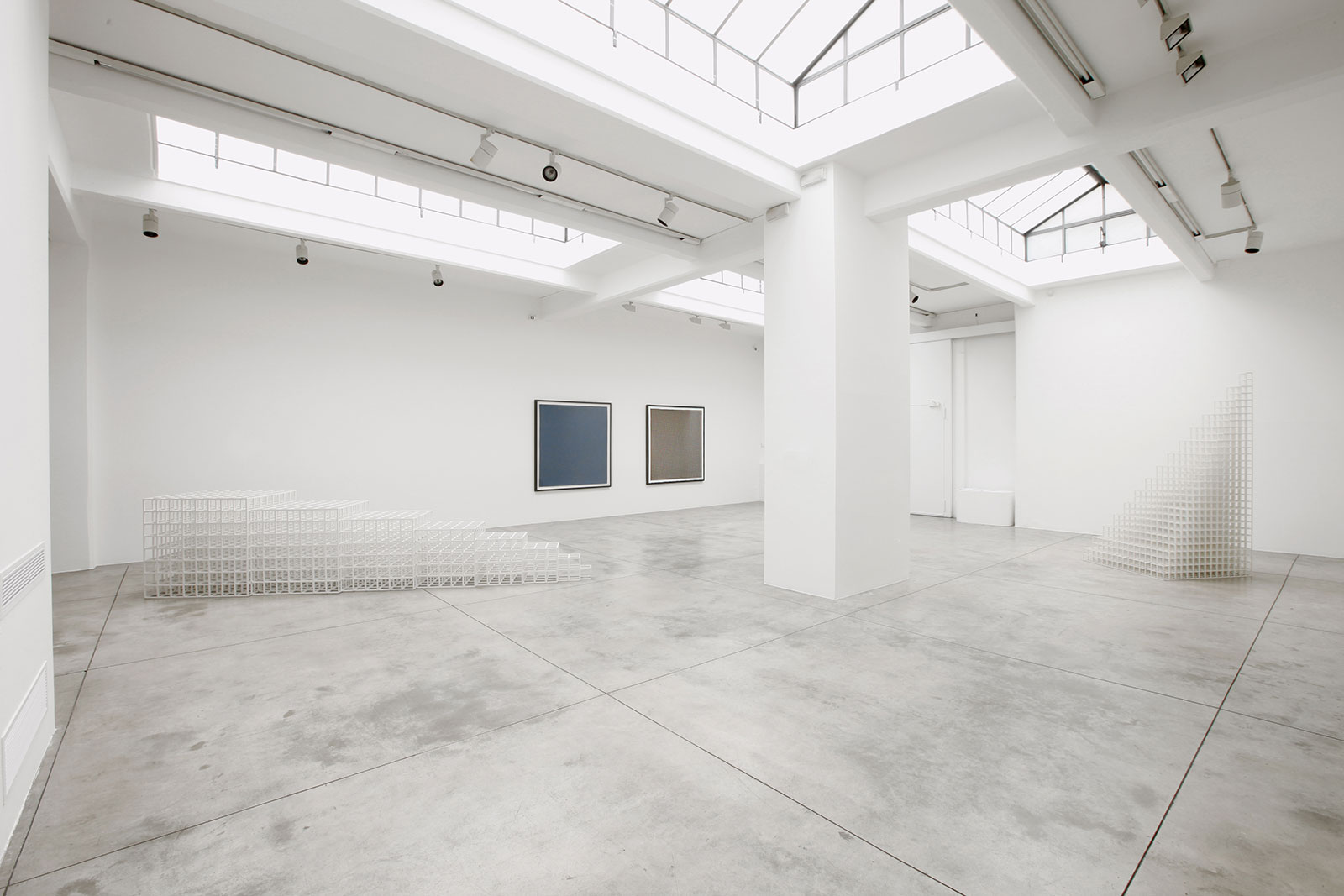
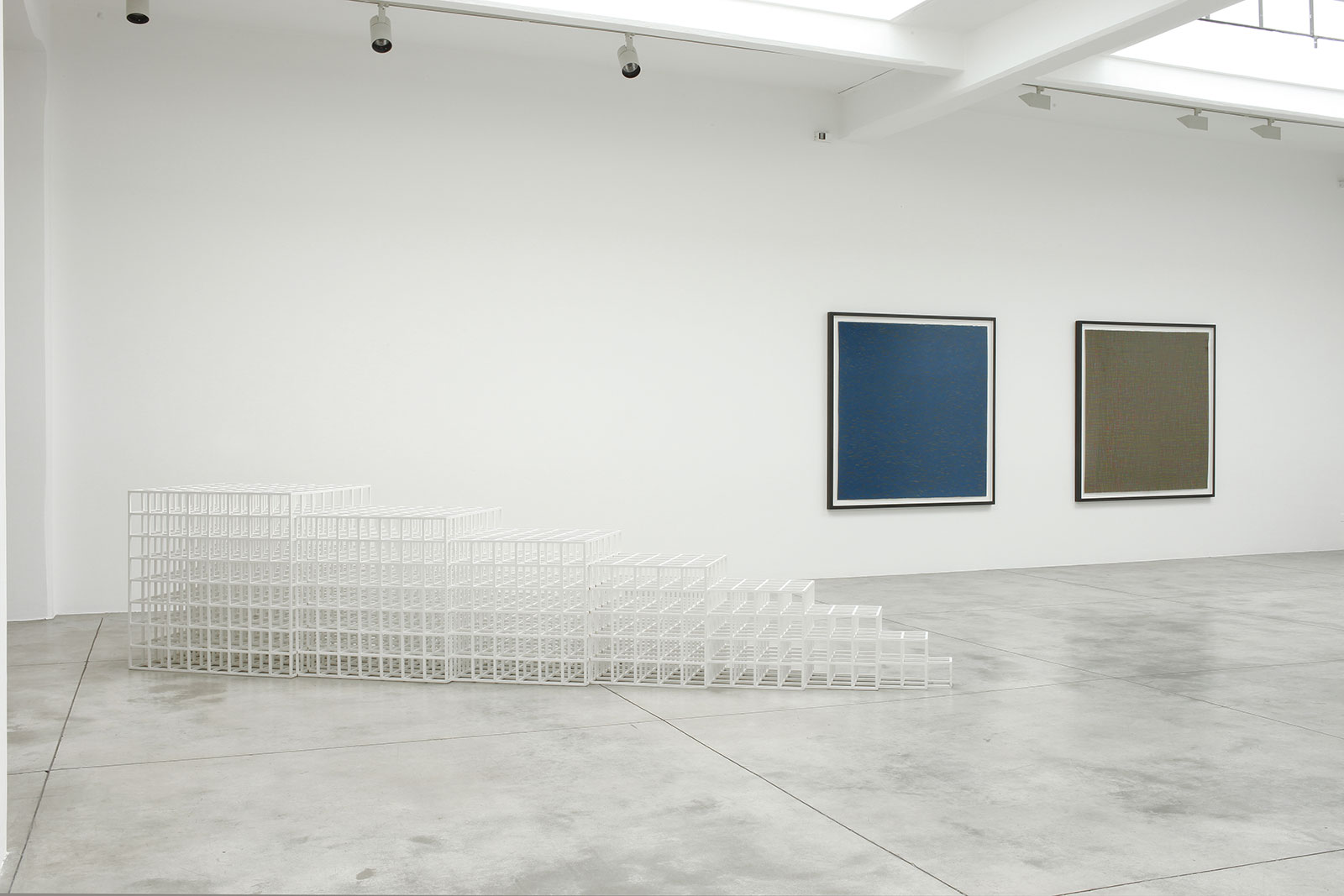
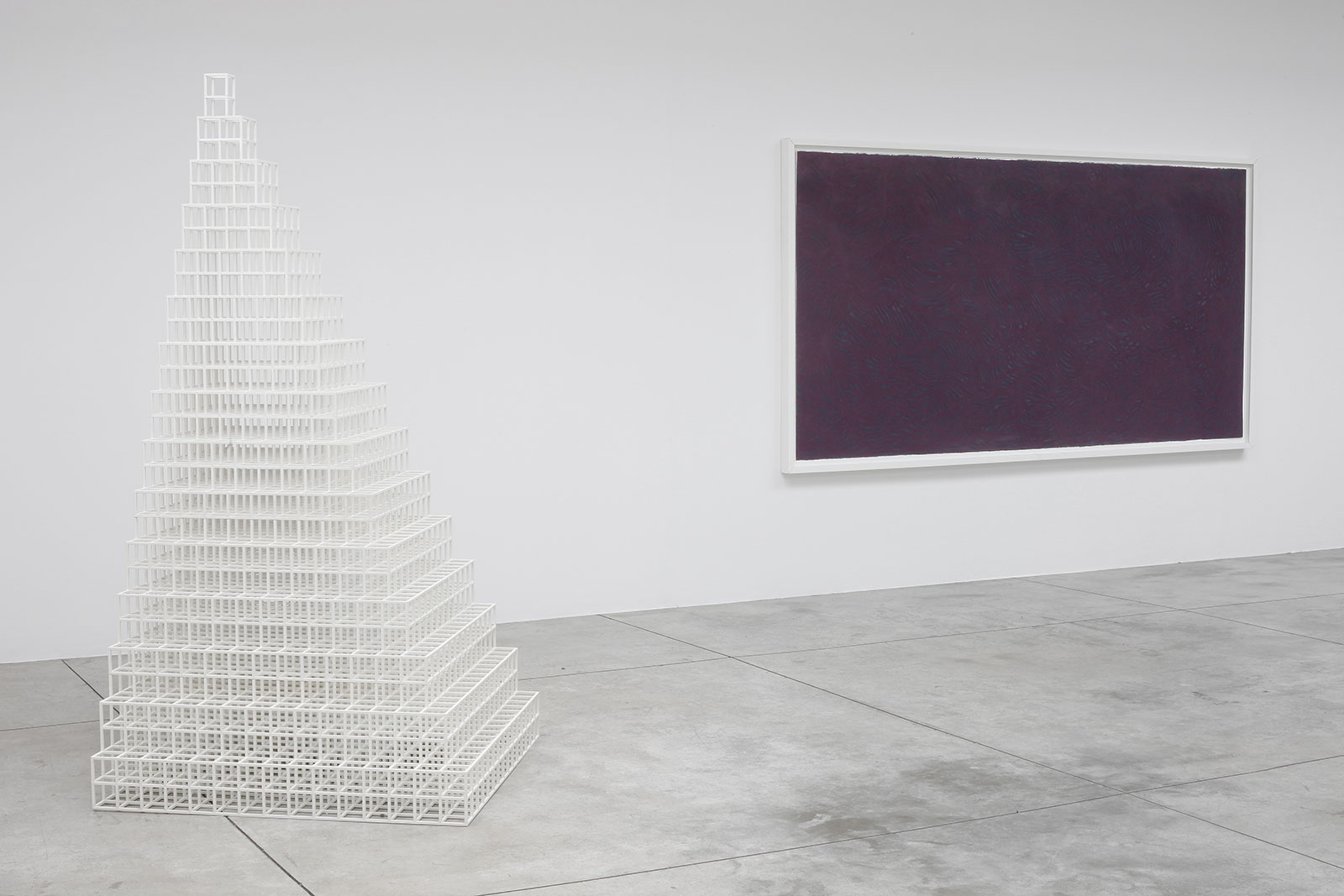
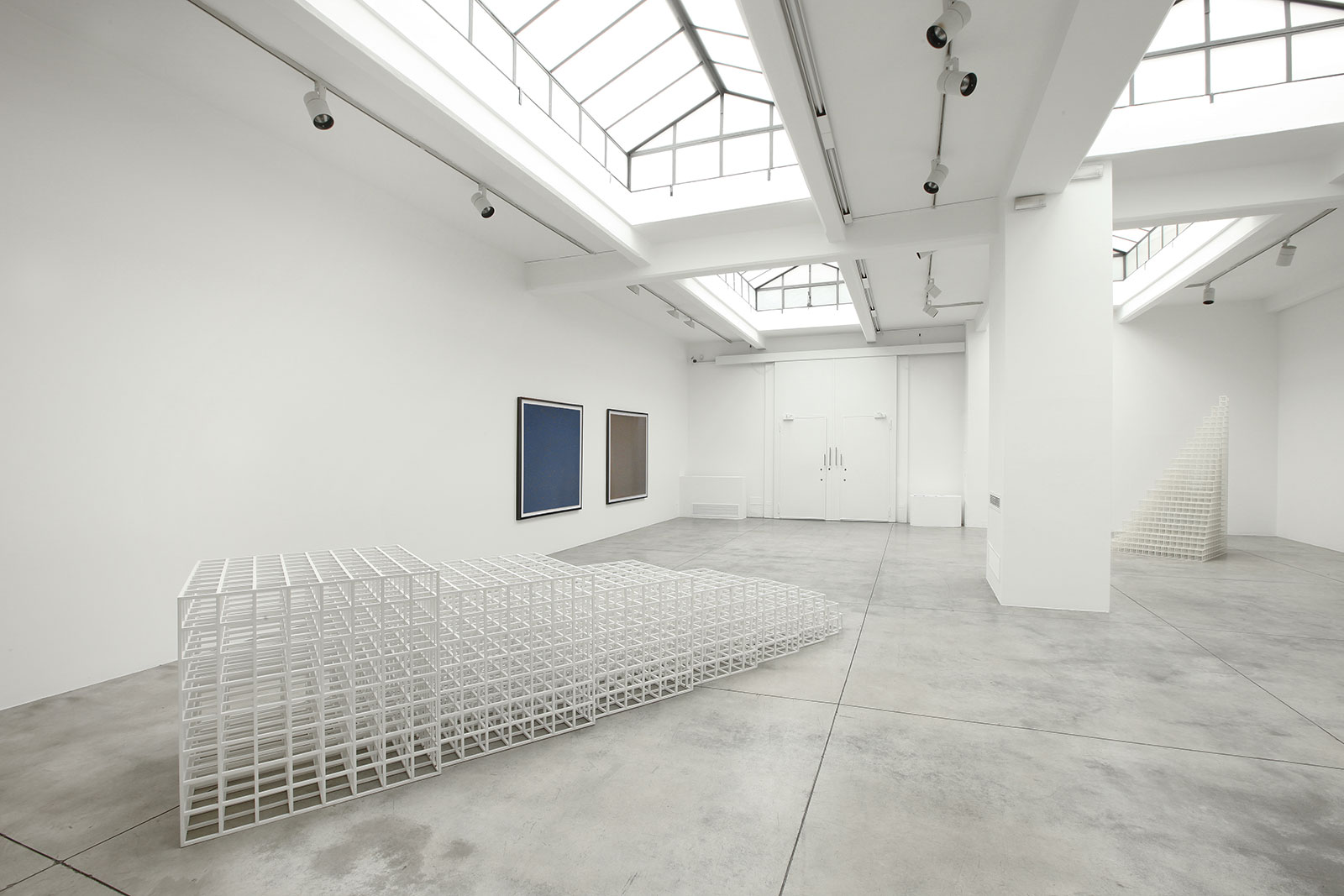
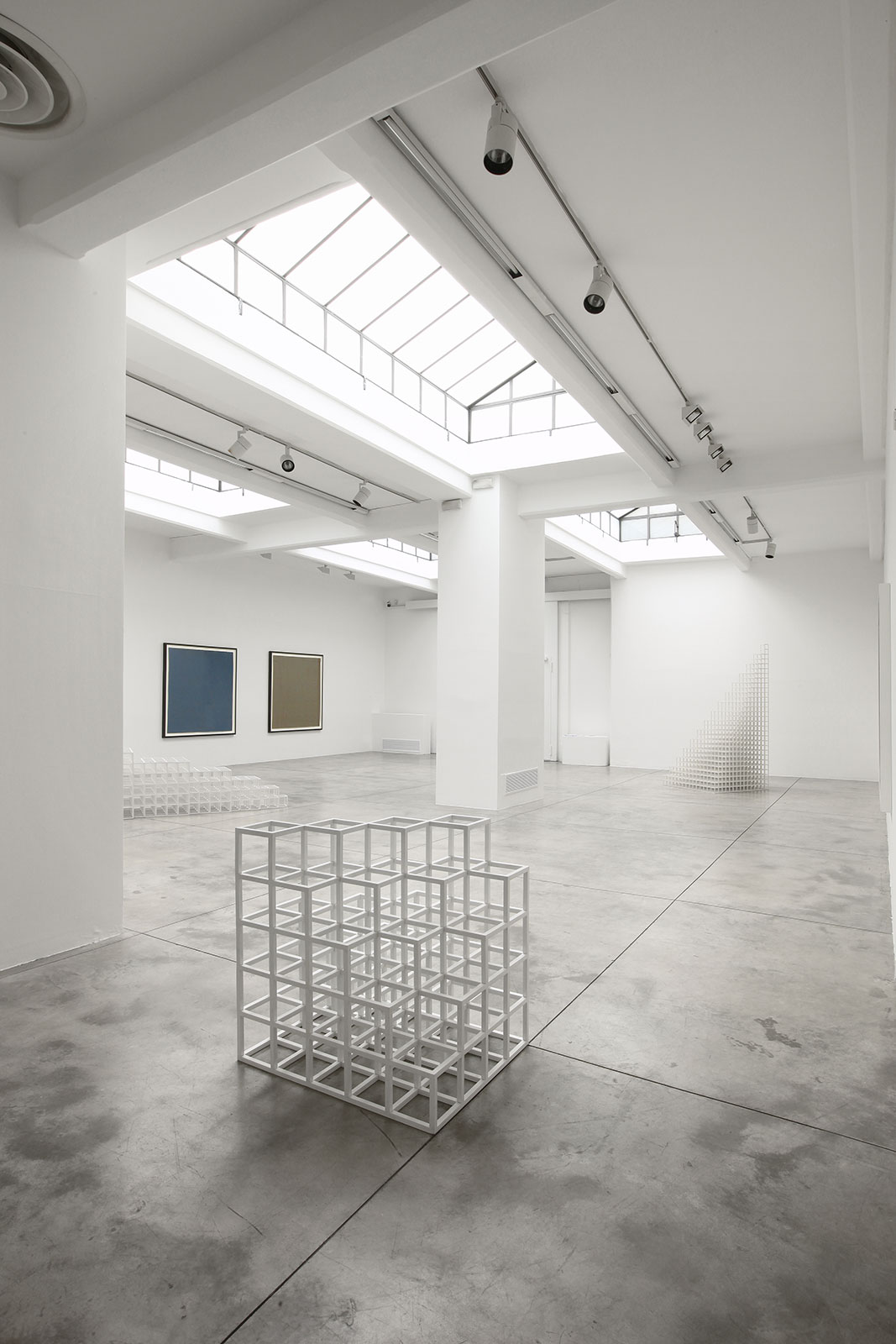
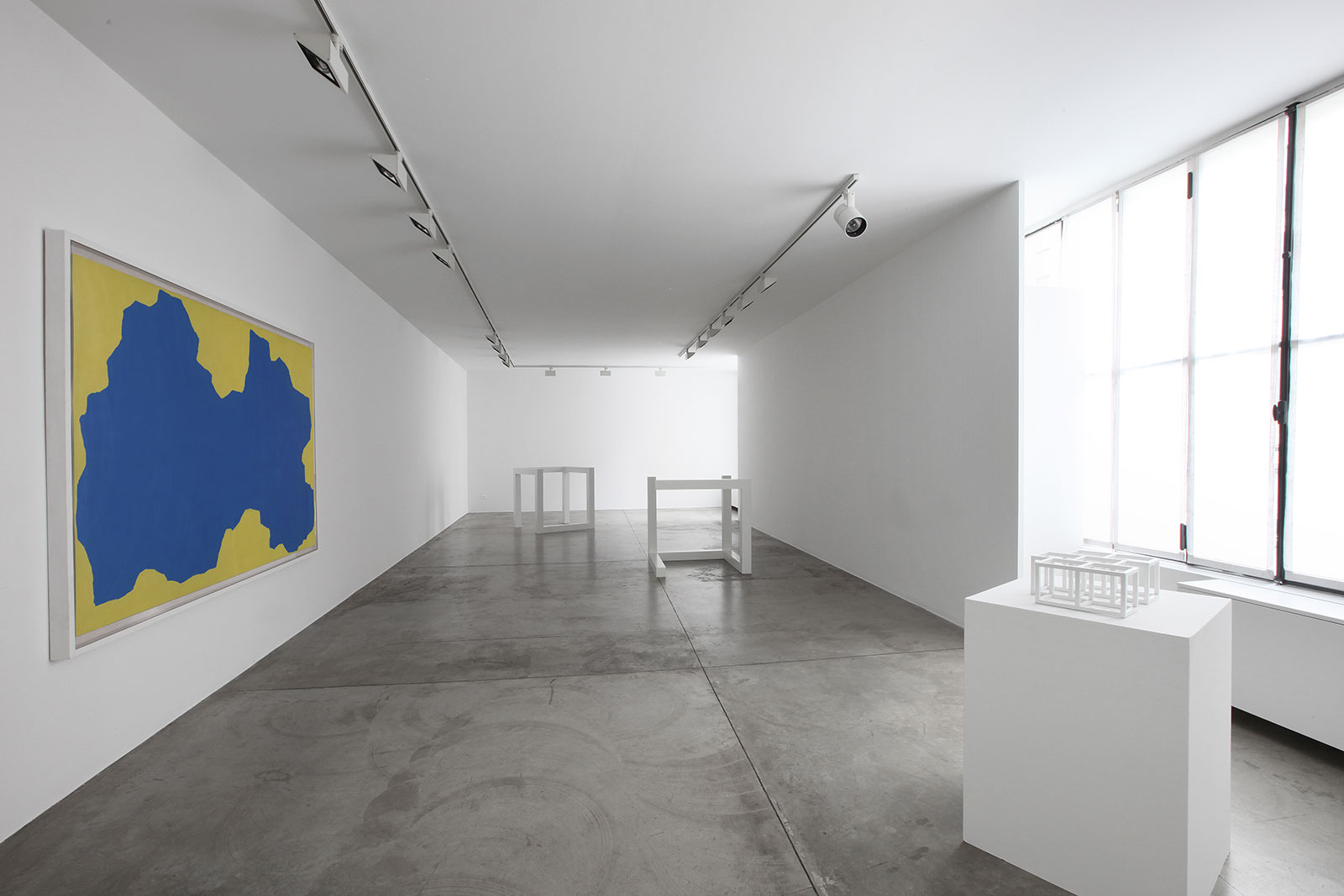
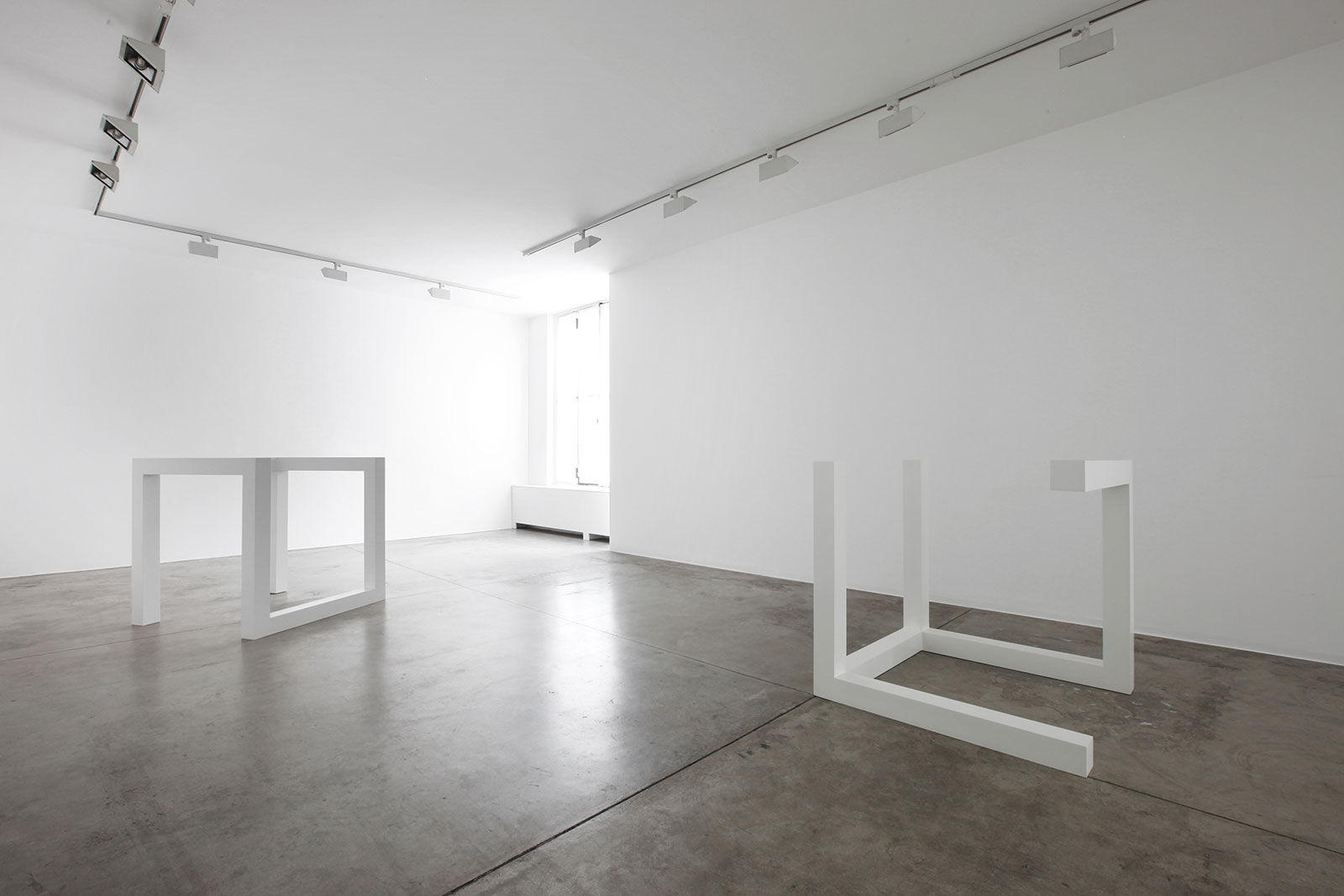
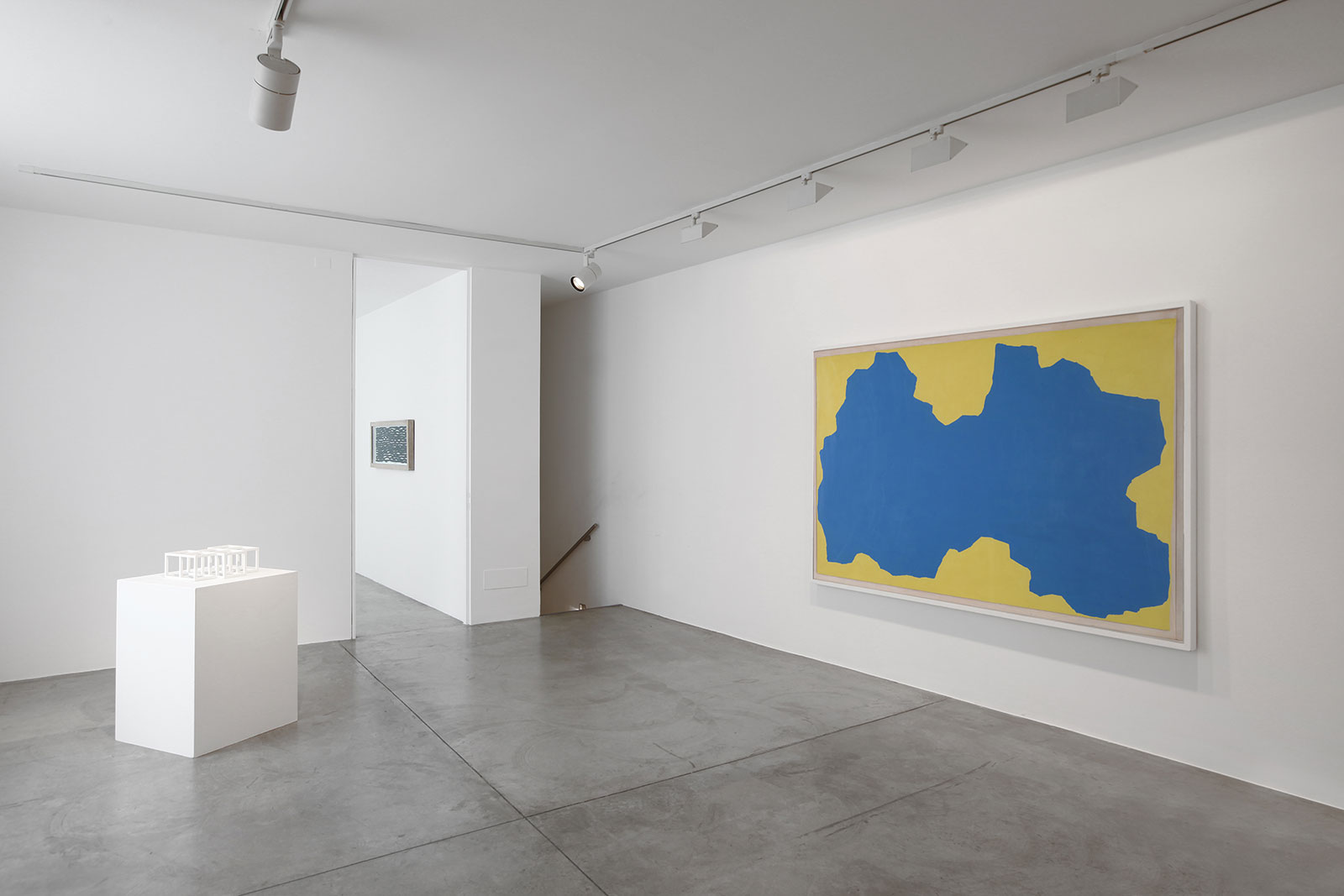
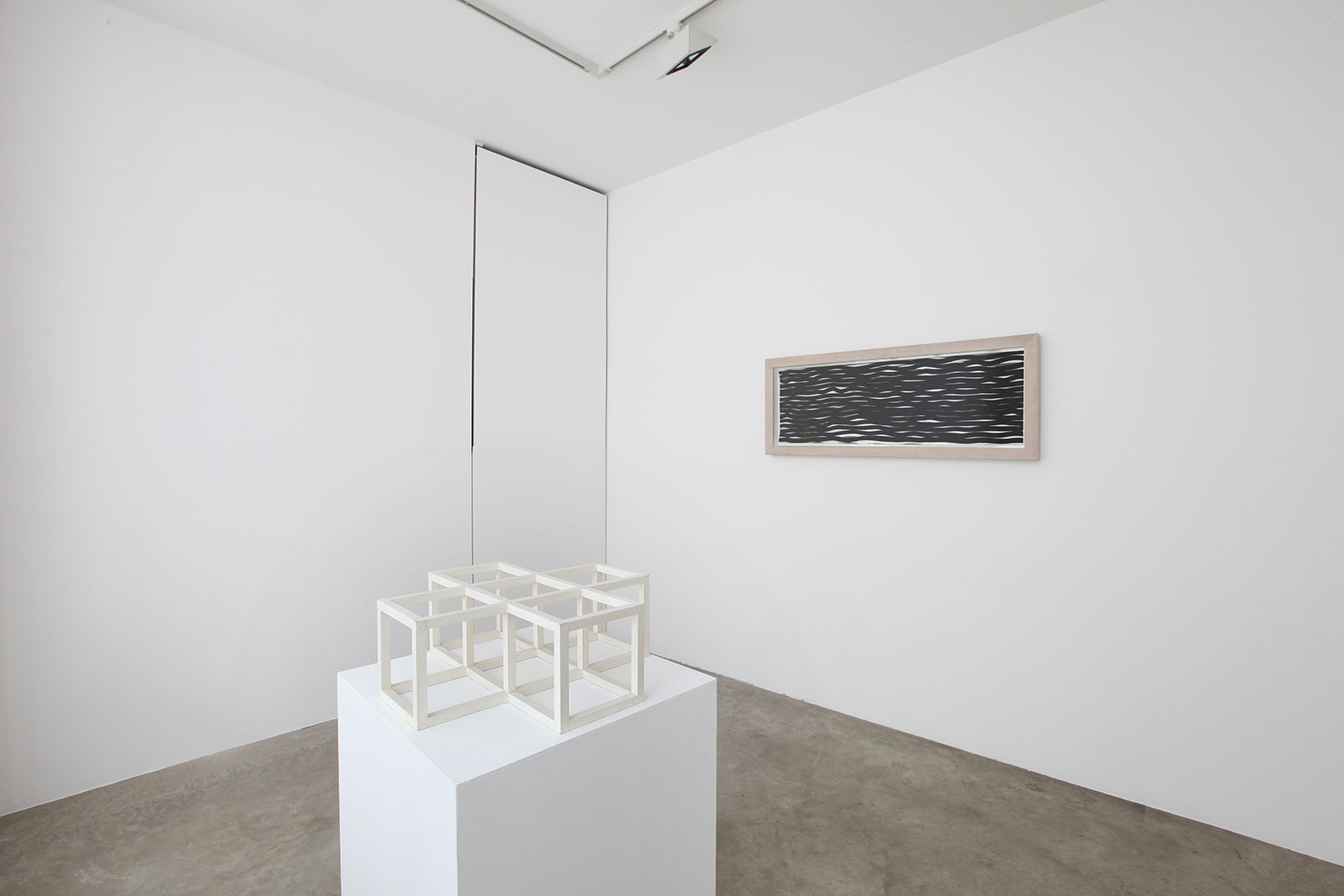
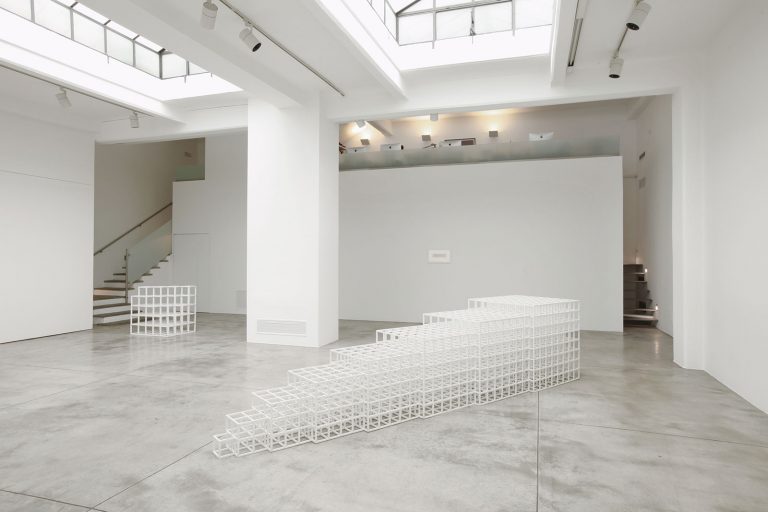
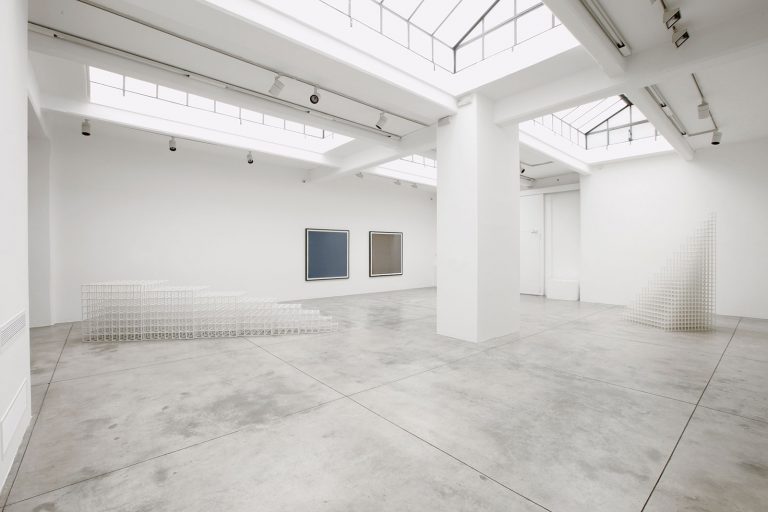
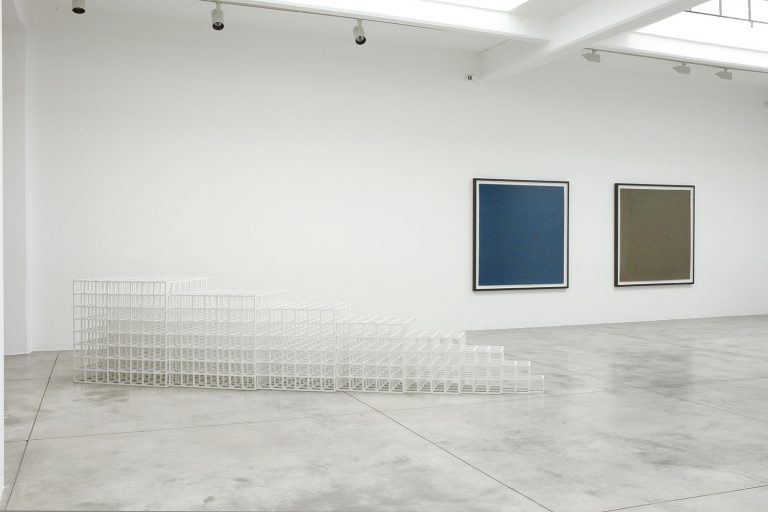
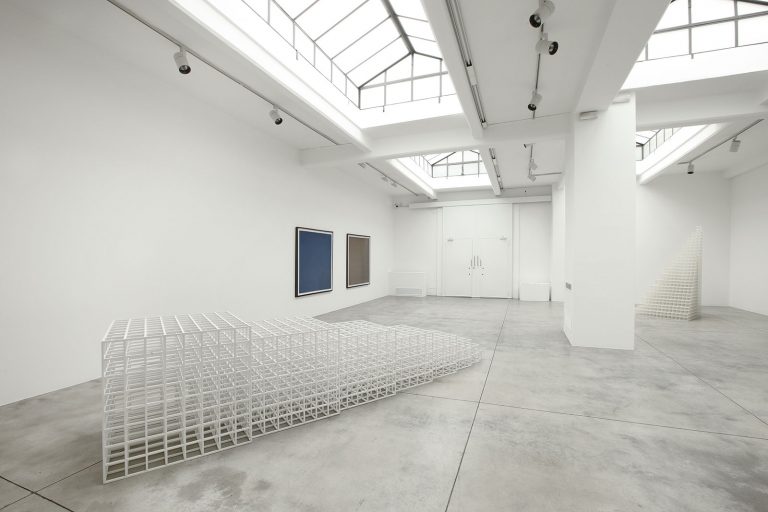
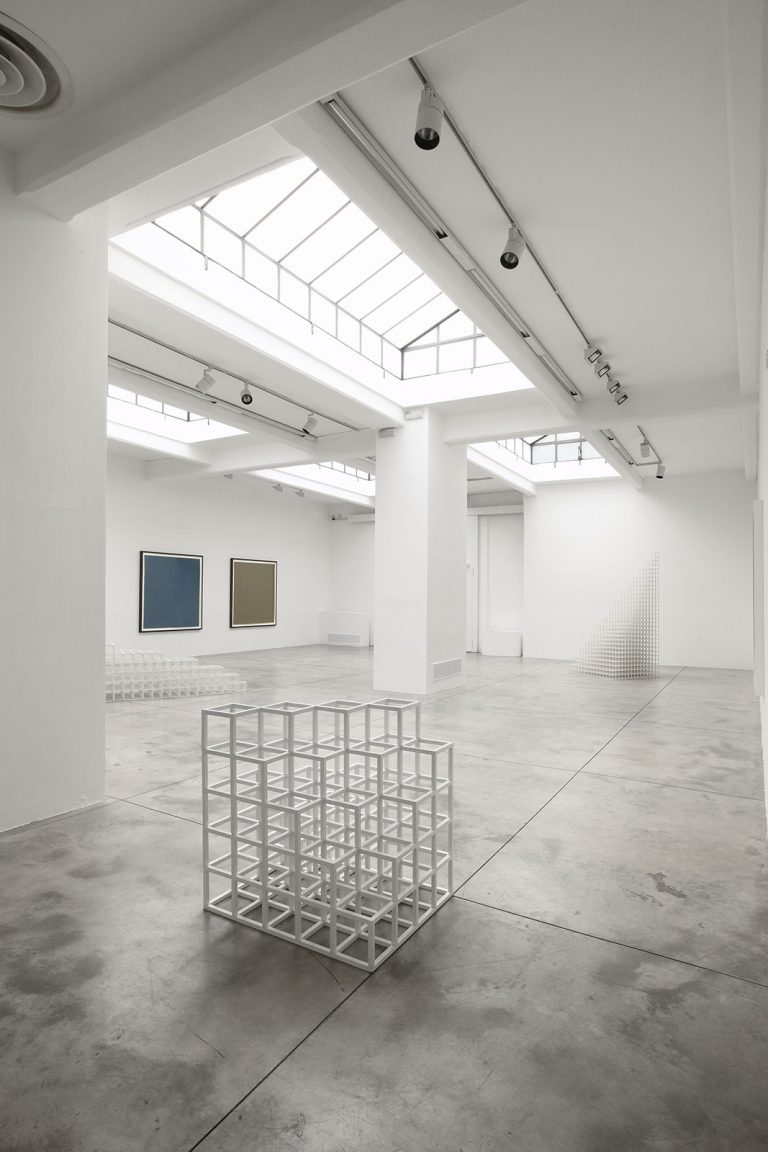
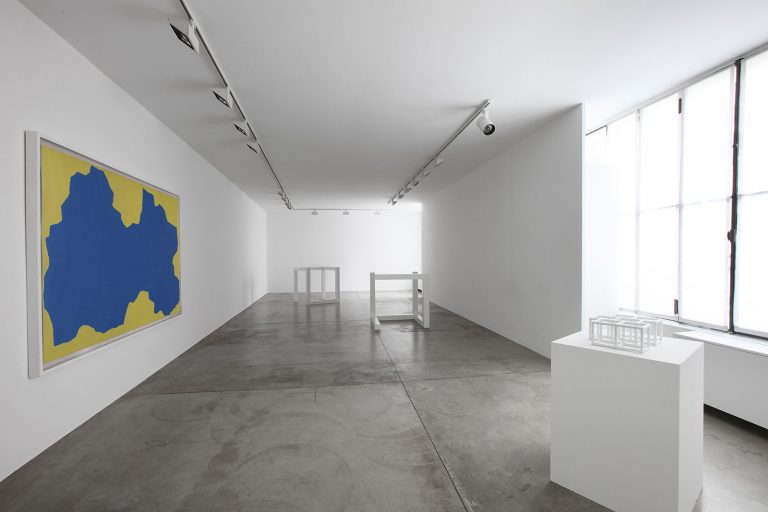




















Cardi Gallery in Milan, is pleased to present Sol LeWitt. On display a selection of 13 works from the 60s to the 2000s
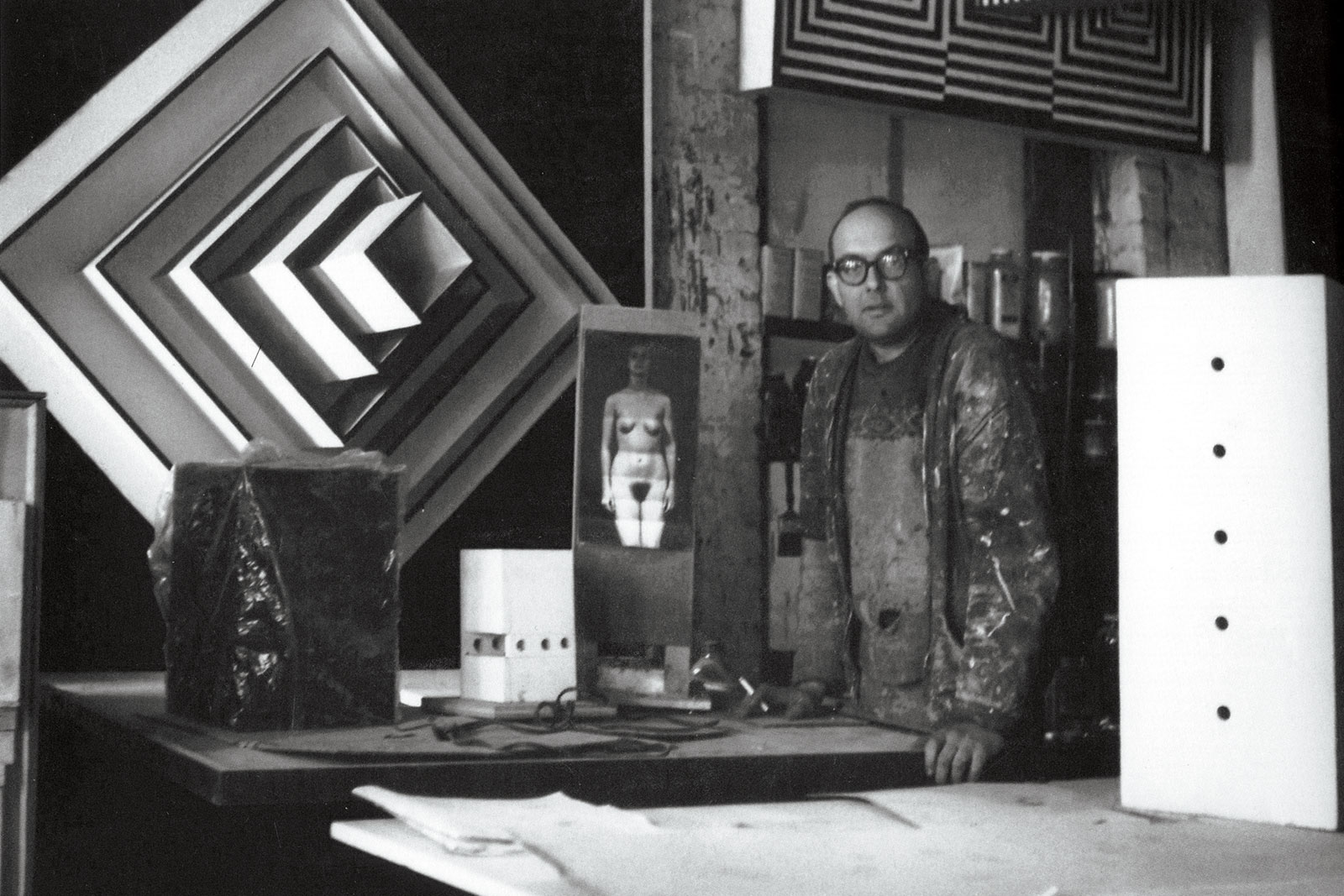
Sol LeWitt (b.1928, Hartford, CT; d. 2007, New York) is a leading figure of Minimalism and pioneer of Conceptual art. Redefining art production by exploring ideas rather than conventional aesthetics, he distilled art to its essentials. Based on mental structures and concrete visual structures, his work was characterized by a constant spirit of inquiry, resulting in unquestionably and invariably original work. In his long artistic career, LeWitt managed to achieve a perfect balance between perceptual and conceptual quality, between the simplicity of geometric order and the search for beauty and intuitive creativity.
LeWitt was pivotal in the creation of the new radical aesthetic of the 1960’s that was a revolutionary contradiction to the ‘Abstract Expressionism’ current in the 1950’s and 60’s New York school. He overturned the conventional rules of artistic practice and of the material production of artworks, dismissing, with his conceptual approach, notions of non-repeatability and of the importance of manual ability, attributing absolute priority to the idea: “The work is the manifestation of an idea. It is an idea and not an object”.
In LeWitt’s view, his work was not essentially a manual practice but was first and foremost a question of producing a pure, Platonic idea, which could then be handed over to someone else for material execution, provided his instructions and the intentions of his idea were respected. In 1967, after taking part in the show at the Jewish Museum di New York, he wrote ‘Paragraphs on Conceptual Art’. “If the artist carried through his idea and makes it into visible form, then all the steps in the process are of importance. The idea itself, even if not made visual, is as much a work of art as any finished product”. Stated LeWitt. “All intervening steps, scribbles, sketches, drawings, failed work models, studies thoughts, conversations, are of interest. Those that show the thought process of the artist are sometimes more interesting than the final product”. (LeWitt, ‘Paragraphs on Conceptual Art’, Artforum Vol.5, no. 10, Summer 1967, pp. 79-83). This “making an idea the work” has meant that the output of this magnificent American artist can now be found around the world – in leading museums, public buildings, private homes, foundations and even in remote universities.
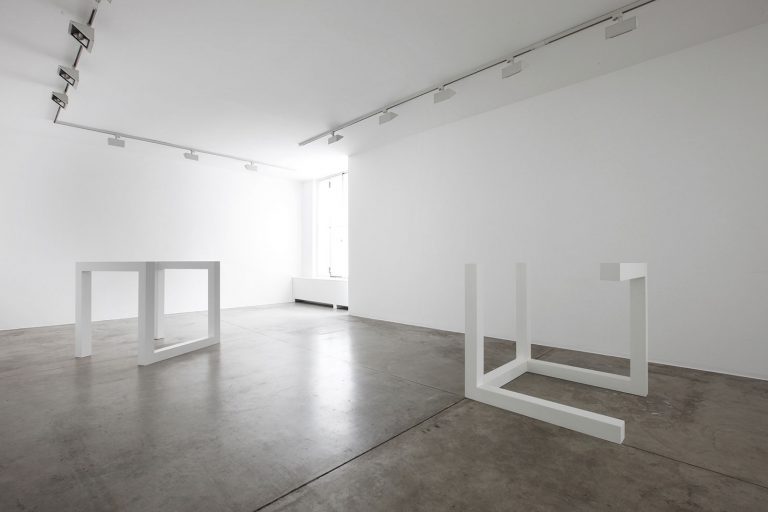
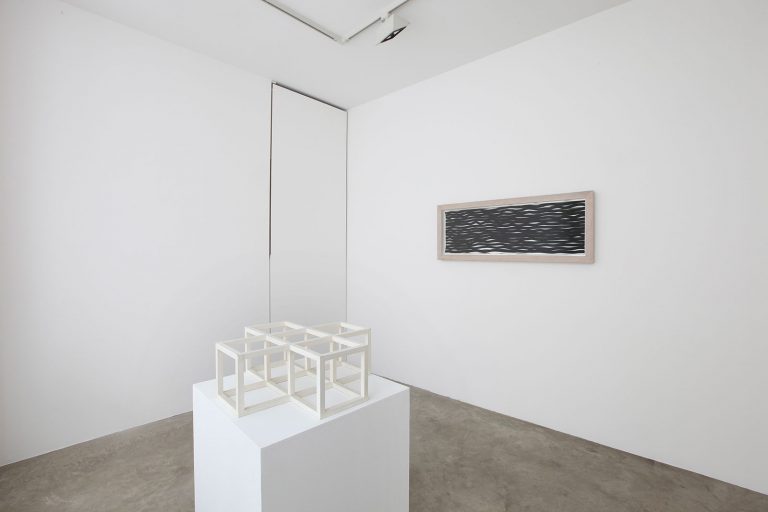
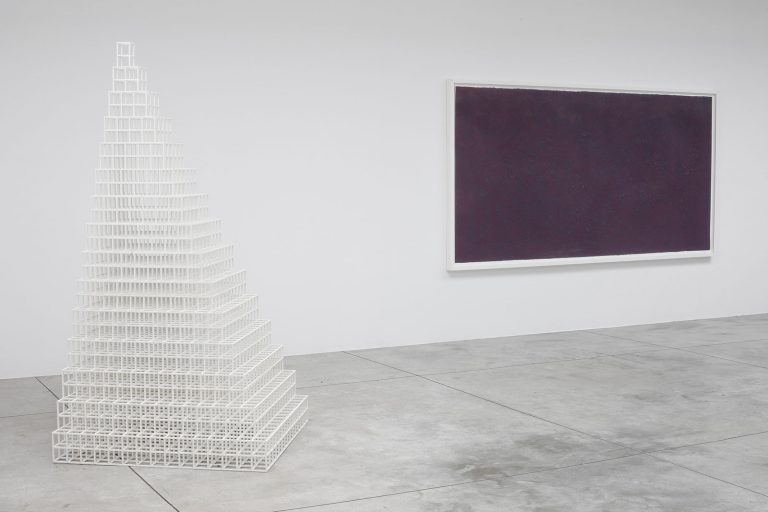
The first part of the masters’ artistic production was Minimalist and pivoted around the geometric figure of the cube: in order to be able to activate and utilize “form” as a “means,” LeWitt elected to work with basic shapes, such as cubes (whether solid, open or skeletal) and lines, that might function as modules, elements that are at once independent and interdependent, a visual lexicon always subject to LeWitt’s artistic syntax and grammar. By the same token, LeWitt’s ‘concepts’ were generally quite simple (“ludicrously simple,” in LeWitt’s own estimation), consisting, for instance, of simple numeric progressions or sequences of colour combinations. The visible, tangible, results, however, the delicate lattices, the muscular installations, the mind-boggling and genre-breaching series of permutations, were not simple at all, but rather beautifully complex and complexly beautiful, delights for both the intellect and the eye, often achieving what Smithson referred to as “intersections with infinity”.
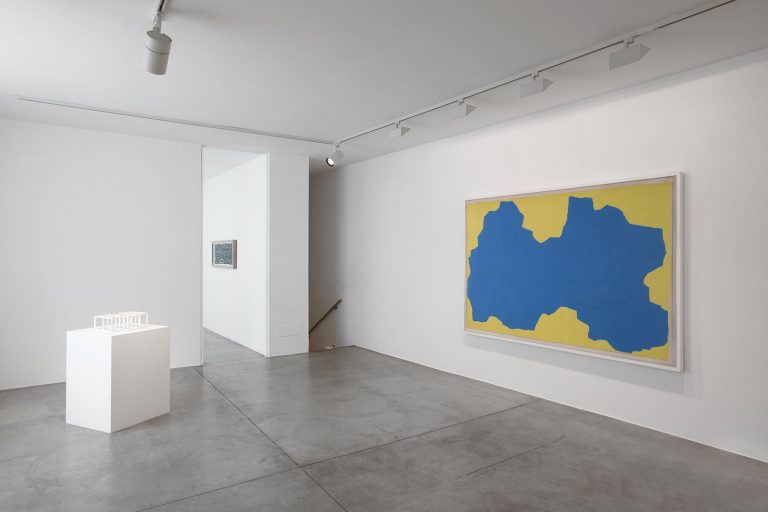
In 1968, LeWitt began to conceive sets of guidelines or simple diagrams for his two-dimensional works drawn directly on the wall, executed first in graphite, then in crayon, later in colored pencil and finally in chromatically rich washes of India ink, bright acrylic paint, and other materials. In the 1980s, in particular after a trip to Italy, LeWitt started using gouache, an opaque water-based paint, to produce free-flowing abstract works in contrasting colours. These represented a significant departure from the rest of his practice, as he created these works with his own hands. LeWitt’s gouaches are often created in series based on a specific motif. The structural principle of LeWitt’s artistic production is the ars combinatoria: cubes, circles, triangles, pyramids and lines, or, as in this case, rectangles and parallelograms are dismantled, reiterated and modulated according to standardized spatial proportions and combined in new ways. The artist reinvented the artistic process, playing on the variability and intermittency of the geometric structures that underpin Western notions of space.
Corso di Porta Nuova 38
Milan, 20121, Italy